///Effects of Thermal Deformation in #WAAM Applied as Stiffeners for Thin Steel Plates
Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (#WAAM) offers exciting possibilities for forming and reinforcing lightweight steel panels, especially in free-form architectural applications. However, controlling thermal deformation remains one of the critical challenges within this technology. Understanding and addressing these effects is essential to unlocking the full potential of WAAM for structural components in the AEC industry.
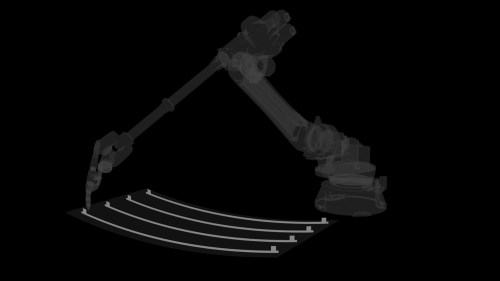
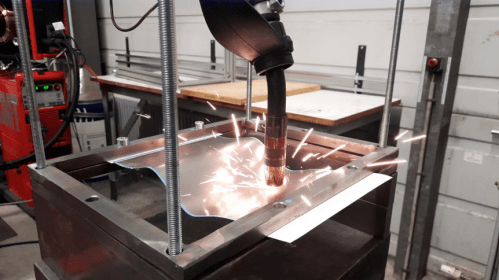
One of the biggest challenges with #WAAM on thin sheet metal is thermal deformation. The videos illustrate this effect on a thin steel plate. As each weld bead and layer is deposited, localized heating and cooling cycles induce significant thermal stresses, resulting in deformation of the plate.
This phenomenon highlights how factors such as fixation systems, process parameters, robotic welding paths, and deposition strategies can critically impact the final geometry of the part. Small variations in any of these variables can result in significant differences in distortion patterns and overall dimensional accuracy.
Overcoming these challenges is key to improving the effectiveness of #WAAM in forming and stiffening lightweight steel panels for free-form facades. Controlling thermal stresses during deposition not only improves geometric accuracy but also ensures the structural performance required for demanding architectural applications.
The work presented here was developed by Juan Ojeda as part of the research project FORMlight.
Short video: here




